What is a Solar Container and How Does it Work?
As the world transitions towards sustainable energy solutions, the concept of a "solar container" has emerged. This innovative technology harnesses solar energy in a compact, portable format. Experts like Dr. Emily Chen, a leading authority in renewable energy, state, “Solar containers provide an effective way to democratize energy access.”
A solar container typically integrates solar panels, storage batteries, and an inverter within a shipping container. This design makes them versatile and suitable for remote locations. They can power everything from construction sites to disaster relief efforts. However, the implementation can be complex and costly, requiring careful consideration of local energy needs.
While solar containers present a promising solution, challenges exist. Efficiency can vary based on weather conditions and geographical location. Moreover, the initial investment may deter some potential users. As the industry evolves, continuous reflection on these obstacles is essential for maximizing the potential of solar containers.
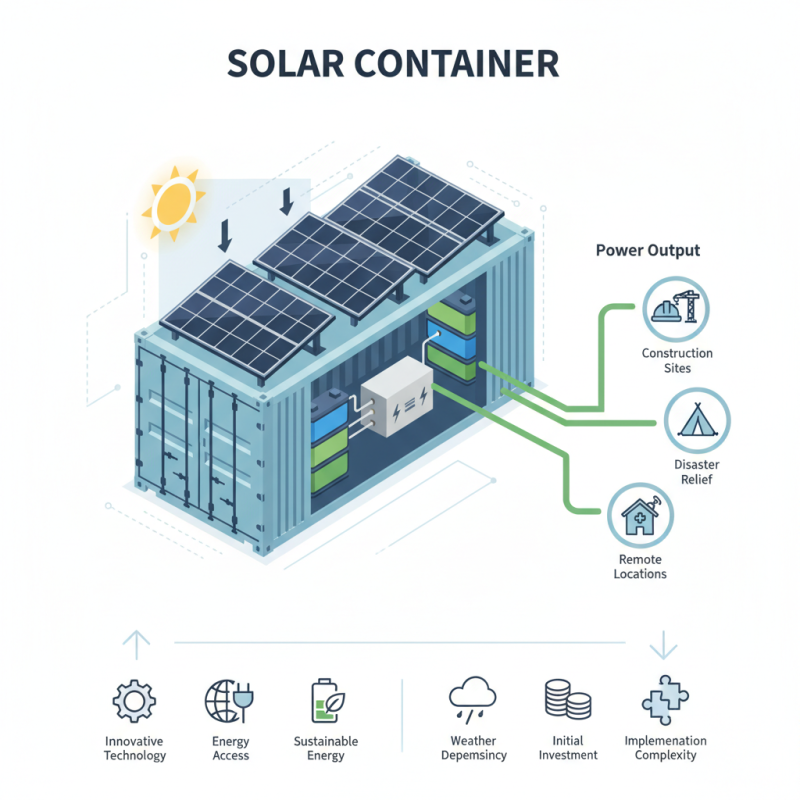
What is a Solar Container?
A solar container is an innovative portable solution for energy needs. It typically consists of solar panels mounted on a shipping container. This design can efficiently harness solar energy. The energy collected is used for various applications, such as powering electronic devices, providing electricity in remote areas, and supporting construction sites.
These containers can be deployed almost anywhere. They are ideal for locations lacking reliable power. However, they may not generate enough energy at night or during cloudy weather. Planning is essential to maximize their efficiency and effectiveness.
Tip: Always assess your energy needs before investing in a solar container. It’s crucial to understand how much power you require daily.
Maintenance is key. Dust and debris can reduce solar panel efficiency. Regular cleaning can help maintain optimal performance. Ensure that the container is placed in a location with maximum sunlight exposure.
Tip: Experiment with different angles for solar panel placement to find the most effective position. It’s okay to reassess your setup and make adjustments over time. Learning and adapting is part of the process.
Key Components of a Solar Container System
A solar container system integrates several key components to harness solar energy efficiently. At its core is a robust solar panel setup, typically using photovoltaic cells. These cells convert sunlight into electricity. Reports suggest that solar panel efficiency has improved significantly, averaging around 20% in recent years. This advancement boosts energy generation, making solar containers more viable.
Energy storage is another crucial element. Most solar container systems include lithium-ion batteries. These batteries store excess energy for later use. Data from energy reports indicate that battery costs have dropped by nearly 89% since 2010. While this price reduction is promising, concerns remain about battery lifecycle and recycling.
The inverter converts the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity. This conversion is vital for most appliances. However, inverters can be less efficient, reaching about 90% efficiency, often leading to energy loss. Moreover, unlike other systems, solar containers can also include smart management systems. These systems optimize energy use and monitor performance, yet they can introduce complexity. The integration of these components requires careful planning and may not always lead to guaranteed outcomes.
How Solar Containers Generate and Store Energy
Solar containers are innovative solutions for energy generation and storage. They combine solar panels with storage batteries, making renewable energy accessible. These containers can be used in remote areas or during disasters. They offer flexibility and mobility, which traditional solar setups often lack.
When sunlight hits the solar panels, it generates electricity. This energy can power homes or charge batteries within the container. The stored energy is utilized when sunlight is not available. However, not all solar containers are equally effective. Location, weather, and system design affect performance. Monitoring energy output is crucial for optimizing use.
Many solar containers face challenges regarding efficiency. Weather conditions can reduce energy generation. Sometimes, limited storage capacity means excess energy goes unused. It’s vital for users to consider these factors. Understanding the potential and limitations can lead to better energy management. Ultimately, solar containers represent a promising step toward sustainable energy.
Applications of Solar Containers in Various Industries
Solar containers are becoming increasingly popular across various industries. They offer a flexible and sustainable solution to energy needs. Reports show that the global market for solar-powered containers is expected to grow significantly. The market was valued at approximately $11 billion in 2022, with a projected annual growth rate of 15% through 2030. This growth reflects a growing awareness of renewable energy sources.
In the construction industry, solar containers serve as portable power stations. They can provide electricity for tools and lighting on job sites. This is particularly useful in remote areas. Studies indicate that up to 30% of construction project delays are due to power supply issues. Solar containers can reduce these delays. Their compact design allows for easy transport. However, some projects struggle to integrate this technology effectively. Training staff to operate and maintain solar containers can be a challenge.
The agricultural sector also benefits from solar containers. They can power irrigation systems and sensors. A recent survey revealed that farmers who use solar energy report a 25% reduction in operational costs. Yet, there are barriers. Initial investment can be high. Access to financing is limited for some farmers. Even with challenges, the potential for increased efficiency and sustainability is significant.
Benefits and Challenges of Using Solar Containers
Solar containers possess unique benefits and challenges that demand attention. They offer a mobile solution for renewable energy. The Global Solar Council reported that solar energy contributes to about 3% of the global energy mix as of 2022. This number is steadily rising, fueled by the growing adoption of solar technologies, including containers. These portable units can be deployed quickly in various locations. They provide electricity where grid access is limited.
However, challenges remain significant. Solar containers often require substantial upfront investment. A report from the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) highlights that installation costs can be prohibitive, especially in developing regions. Maintenance can also be tricky. Once deployed, the weather can impact efficiency. Moreover, integrating these systems into existing infrastructure poses additional hurdles. The lifecycle of solar panels—typically 25 years—means that long-term planning is essential yet frequently overlooked.
Additionally, local conditions affect energy generation. In some areas, cloudy days can reduce output considerably. Stakeholders should prepare for this variability. Public skepticism about solar technology still exists. Education and community engagement are crucial to overcoming resistance. Engaging local populations may enhance acceptance of solar containers as a sustainable solution.
